1. 문제
11371번: The Big Eye in the Sky (acmicpc.net)
11371번: The Big Eye in the Sky
For each test case, output to a newline the number of degrees (rounded to the closest integer) to rotate the Eye. Note that each test case is rotating from the x-axis, not from the previous orientation of the Eye.
www.acmicpc.net
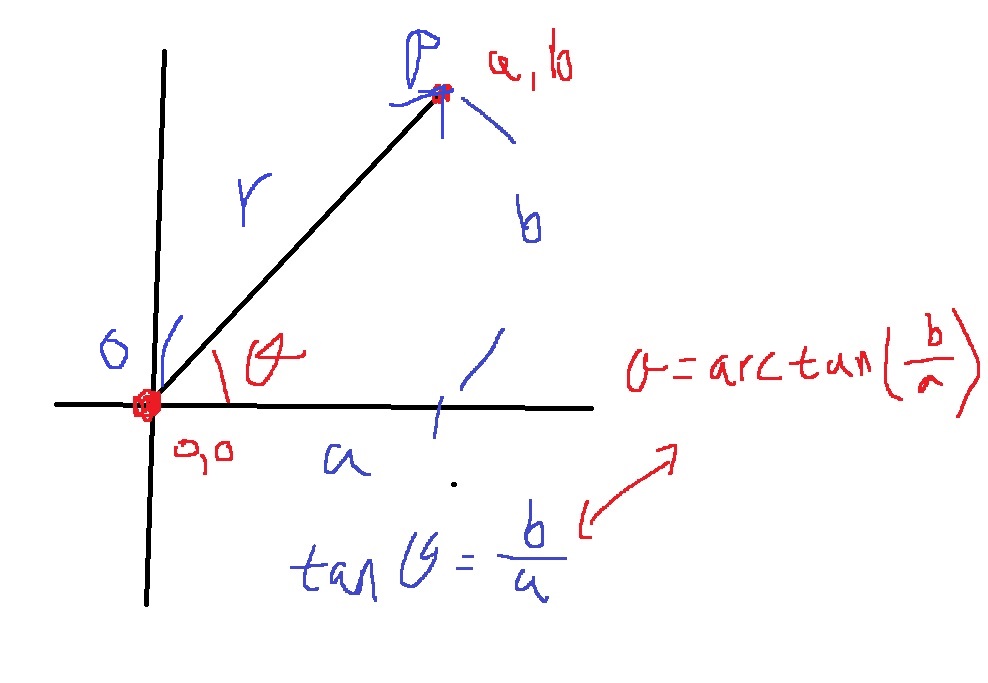
1사분면 위의 (x,y)가 (0,0)과 양의 x축과 이루는 각도를 구하는 문제
2. 풀이
다음 그림과 같이 (a,b)에 대하여 arctan(b/a)를 구하면 될텐데..

다행히 math 모듈에 math.atan()이라는 함수가 존재한다.

사용할때는 결과가 [-pi/2, pi/2]로 나온다는 점을 보고.. 전제가 1사분면(0~pi/2)이니까 일단 범위에 맞다
또한 각도가 아니라, 라디안으로 나온다는 점을 보면 math.degrees()가 라디안을 각도로 바꿔준다

x = 0인 경우 명백히 90도니까 90을 print하고
y = 0인 경우 명백히 0도니까 0을 print
그 외에는 math.degrees(math.atan(y/x))로 구하면 되겠다.
결과가 실수값이기 때문에 정수형으로 바꿔줘야한다.
import math
from sys import stdin
while 1:
x,y = map(int,stdin.readline().split())
if x == 0 and y == 0:
break
if x == 0:
print(90)
elif y == 0:
print(0)
else:
print(int(round(math.degrees(math.atan(y/x)),0)))
아래에서 배울 atan2를 이용한다면, 경우를 나눌필요 없이 간단하게 가능하다.
import math
from sys import stdin
while 1:
x,y = map(int,stdin.readline().split())
if x == 0 and y == 0:
break
print(int(round(math.degrees(math.atan2(y,x)),0)))
3. 문제2
28038번: 2차원 좌표변환 (acmicpc.net)
28038번: 2차원 좌표변환
2차원 공간에서 점의 위치를 표현하는 방식은 여러 가지가 있다. 일반적으로 많이 쓰이는 직교좌표계는 x축, y축 방향의 1차원 위치를 통해 점의 위치를 표현한다. 이 문제에서는 점의 2차원 위치
www.acmicpc.net
4. 풀이
$(r,\theta)$가 주어지면 (x,y)로 바꾸거나 (x,y)가 주어지면 $(r,\theta)$로 바꾸면 되는데
다음과 같은 형태인데 이번엔 $\theta$의 범위가 0부터 2pi까지라서 1사분면만이 아니다.
그래서 math.atan이 아니라 math.atan2를 써야한다.

얘는 arctan 값을 내주는데, 결과가 [-pi,pi]로 나오며, 특징이 좌표 (y,x)순으로 받는다는 특징이 있다.
또한 계산되는 값은 양의 x축과 좌표 (x,y)가 이루는 각이라고 설명하고 있고
마지막 설명을 보면 좌표가 어떤 사분면을 가지는지 알 수 있다고 나오는데
다음과 같이 1,2사분면에서는 양수 0 ~ pi로 나오고 3,4사분면에서는 -pi ~ 0의 음수로 나온다.

하지만 문제에서 원하는건 x축 양의 방향과 OP가 시계 반대방향으로 이루는 각을 원하고 있다
math.atan2가 음수이면 다음과 같이 나오기 때문에 원하는 값을 얻을려면 2pi + math.atan2(y,x)로 구해줘야겠다.

(x,y)로 주어지면 OP를 유클리드 거리로 구하고, arctan값을 구해서 각도를 구해준다.
근데 math.atan2(y,x)는 x,y가 0이냐에 상관없이 계산해주기 때문에 위 문제처럼 x = 0, y = 0인 경우 나눠서 구할 필요는 없다
$(r,\theta)$로 주어진다면? 삼각함수 이용해서 $(rcos(\theta), rsin(\theta))$로 쉽게 구할 수 있다
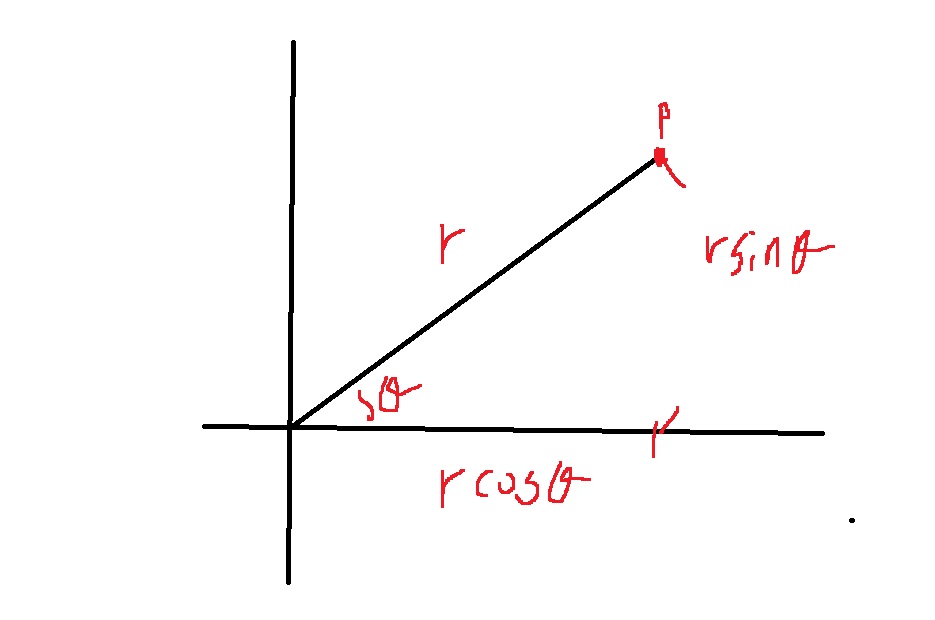
import math
from sys import stdin
def distance(x,y):
return (x**2 + y**2)**(1/2)
def theta(x,y):
t = math.atan2(y,x)
if t < 0:
return 2*math.pi+t
else:
return t
def convert(n,x,y):
if n == 1:
r = distance(x,y)
if r == 0:
return 0,0
else:
return r,theta(x,y)
else:
return x*math.cos(y),x*math.sin(y)
T = int(stdin.readline())
for _ in range(T):
n = int(stdin.readline())
x,y = map(float,stdin.readline().split())
a,b = convert(n,x,y)
print(a,b)
'기하학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 볼록 껍질(convex hull)구하는 monotone chain 알고리즘 배우기 (0) | 2023.09.08 |
|---|---|
| 볼록 껍질(convex hull) 구하는 graham scan 알고리즘 배우기 (0) | 2023.09.07 |
| 다각형 내부의 격자점 수를 셀 수 있을까 - 픽의 정리(pick's theorem) + (선분에 있는 격자점의 개수 세는 방법) (0) | 2023.08.31 |
| 선분의 길이가 주어질때 볼록 다각형(conver polygon)이 될 조건 (0) | 2023.08.25 |
| 정육면체가 쌓인 3차원 도형의 겉넓이를 구하는 방법 (0) | 2023.08.25 |

